First, Internal modulation and external modulation
According to the relative relationship between the modulator and the laser, the laser modulation can be divided into internal modulation and external modulation.
01 internal modulation
The modulation signal is carried out in the process of laser oscillation, that is, the parameters of laser oscillation are changed according to the law of the modulation signal, so as to change the characteristics of the laser output and achieve modulation.
(1) Directly control the laser pump source to achieve the modulation of the output laser intensity and whether there is, so that it is controlled by the power supply.
(2) The modulation element is placed in the resonator, and the change of the physical characteristics of the modulation element is controlled by the signal to change the parameters of the resonator, thus changing the output characteristics of the laser.
02 External modulation
External modulation is the separation of laser generation and modulation. Refers to the loading of the modulated signal after the formation of the laser, that is, the modulator is placed in the optical path outside the laser resonator.
The modulation signal voltage is added to the modulator to make some physical characteristics of the modulator phase change, and when the laser passes through it, some parameters of the light wave are modulated, thus carrying the information to be transmitted. Therefore, external modulation is not to change the laser parameters, but to change the parameters of the output laser, such as intensity, frequency, and so on.
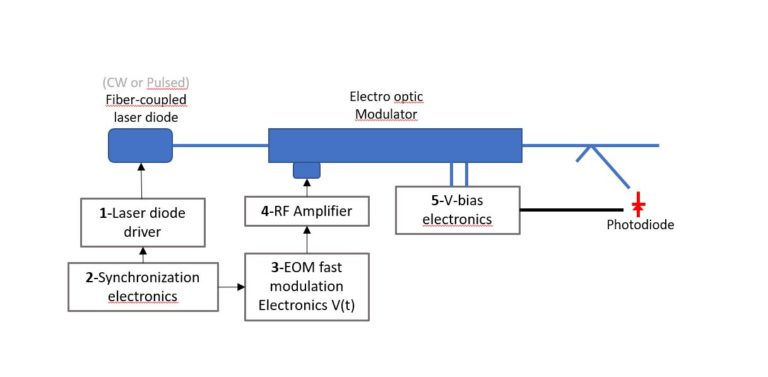
Second, laser modulator classification
According to the working mechanism of the modulator, it can be classified into electro-optic modulation, acoustooptic modulation, magneto-optic modulation and direct modulation.
01 Direct modulation
The driving current of the semiconductor laser or light-emitting diode is modulated directly by the electric signal, so that the output light is modulated with the change of the electrical signal.
(1) TTL modulation in direct modulation
A TTL digital signal is added to the laser power supply, so that the laser drive current can be controlled through the external signal, and then the laser output frequency can be controlled.
(2) Analog modulation in direct modulation
In addition to the laser power supply analog signal (amplitude less than 5V arbitrary change signal wave), can make the external signal input different voltage corresponding to the laser different drive current, and then control the output laser power.
02 Electro-optic modulation
Modulation using electro-optic effect is called electro-optic modulation. The physical basis of electro-optic modulation is the electro-optic effect, that is, under the action of an applied electric field, the refractive index of some crystals will change, and when the light wave passes through this medium, its transmission characteristics will be affected and changed.
03 Acousto-optic modulation
The physical basis of acousto-optic modulation is the acousto-optic effect, which refers to the phenomenon that light waves are diffused or scattered by the supernatural wave field when propagating in the medium. When the refractive index of a medium changes periodically to form a refractive index grating, diffraction will occur when the light wave propagates in the medium, and the intensity, frequency and direction of the diffractive light will change with the change of the supergenerated wave field.
Acousto-optic modulation is a physical process that uses acousto-optic effect to load information on the optical frequency carrier. The modulated signal is acted on the electro-acoustic transducer in the form of electrical signal (amplitude modulation), and the corresponding electrical signal is converted into ultrasonic field. When the light wave passes through the acousto-optic medium, the optical carrier is modulated and becomes an intensity modulated wave that “carries” information.
04 Magneto-optical modulation
Magneto-optic modulation is an application of Faraday’s electromagnetic optical rotation effect. When light waves propagate through the magneto-optical medium parallel to the direction of the magnetic field, the phenomenon of rotation of the polarization plane of linearly polarized light is called magnetic rotation.
A constant magnetic field is applied to the medium to achieve magnetic saturation. The direction of the circuit magnetic field is in the axial direction of the medium, and Faraday rotation depends on the axial current magnetic field. Therefore, by controlling the current of the high-frequency coil and changing the magnetic field strength of the axial signal, the rotation Angle of the optical vibration plane can be controlled, so that the light amplitude through the polarizer changes with the change of θ Angle, so as to achieve modulation.
Post time: Jan-08-2024





