Tuning principle of Tunable semiconductor laser (Tunable laser)
Tunable semiconductor laser is a kind of laser which can continuously change the wavelength of laser output in a certain range. Tunable semiconductor laser adopts thermal tuning, electrical tuning and mechanical tuning to adjust the cavity length, grating reflection spectrum, phase and other variables to achieve wavelength tuning. This kind of laser has a wide range of applications in optical communication, spectroscopy, sensing, medical and other fields. Figure 1 shows the basic composition of a tunable laser, including the light gain unit, the F-P cavity composed of the front and rear mirrors, and the optical mode selection filter unit. Finally, by adjusting the length of the reflection cavity, the optical mode filter can reach the wavelength selection output.
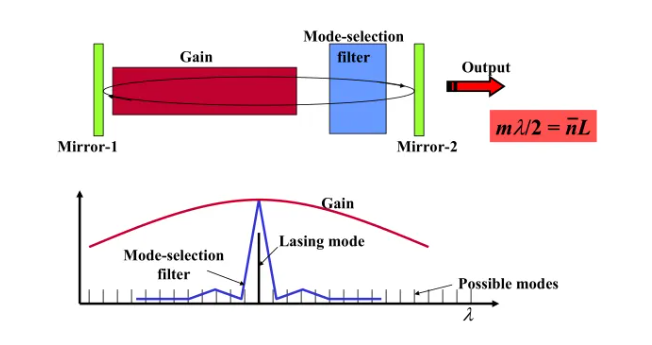
FIG.1
Tuning method and its derivation
The tuning principle of tunable semiconductor lasers mainly depends on changing the physical parameters of the laser resonator to achieve continuous or discrete changes in the output laser wavelength. These parameters include, but are not limited to, refractive index, cavity length, and mode selection. The following details several common tuning methods and their principles:
1. Carrier injection tuning
Carrier injection tuning is to change the refractive index of the material by changing the current injected into the active region of the semiconductor laser, so as to achieve wavelength tuning. When the current increases, the carrier concentration in the active region increases, resulting in a change in refractive index, which in turn affects the laser wavelength.
2. Thermal tuning Thermal tuning is to change the refractive index and cavity length of the material by changing the operating temperature of the laser, so as to achieve wavelength tuning. Changes in temperature affect the refractive index and physical size of the material.
3. Mechanical tuning Mechanical tuning is to achieve wavelength tuning by changing the position or Angle of the external optical elements of the laser. Common mechanical tuning methods include changing the Angle of the diffraction grating and moving the position of the mirror.
4 Electro-optical tuning Electro-optical tuning is achieved by applying an electric field to a semiconductor material to change the refractive index of the material, thereby achieving wavelength tuning. This method is commonly used in electro-optical modulators (EOM) and electro-optically tuned lasers.
In summary, the tuning principle of tunable semiconductor laser mainly realizes wavelength tuning by changing the physical parameters of the resonator. These parameters include refractive index, cavity length, and mode selection. Specific tuning methods include carrier injection tuning, thermal tuning, mechanical tuning and electro-optical tuning. Each method has its own specific physical mechanism and mathematical derivation, and the selection of the appropriate tuning method needs to be considered according to the specific application requirements, such as tuning range, tuning speed, resolution and stability.
Post time: Dec-17-2024





