Optical signal detection hardware spectrometer
A spectrometer is an optical instrument that separates polychromatic light into a spectrum. There are many types of spectrometers, in addition to the spectrometers used in the visible light band, there are infrared spectrometers and ultraviolet spectrometers. According to the different dispersion elements, it can be divided into prism spectrometer, grating spectrometer and interference spectrometer. According to the detection method, there are spectroscopes for direct eye observation, spectroscopes for recording with photosensitive films, and spectrophotometers for detecting spectra with photoelectric or thermoelectric elements. A monochromator is a spectral instrument that outputs only a single chromatographic line through a slit, and is often used in conjunction with other analytical instruments.
A typical spectrometer consists of an optical platform and a detection system. It includes the following main parts:
1. Incident slit: the object point of the imaging system of the spectrometer formed under the irradiation of the incident light.
2. Collimation element: the light emitted by the slit becomes parallel light. The collimating element may be an independent lens, a mirror, or directly integrated on a dispersing element, such as a concave grating in a concave grating spectrometer.
(3) Dispersion element: usually using a grating, so that the light signal in space according to the wavelength dispersion into multiple beams.
4. Focusing element: Focus the dispersive beam so that it forms a series of incident slit images on the focal plane, where each image point corresponds to a specific wavelength.
5. Detector array: placed on the focal plane for measuring the light intensity of each wavelength image point. The detector array can be a CCD array or other kinds of light detector array.
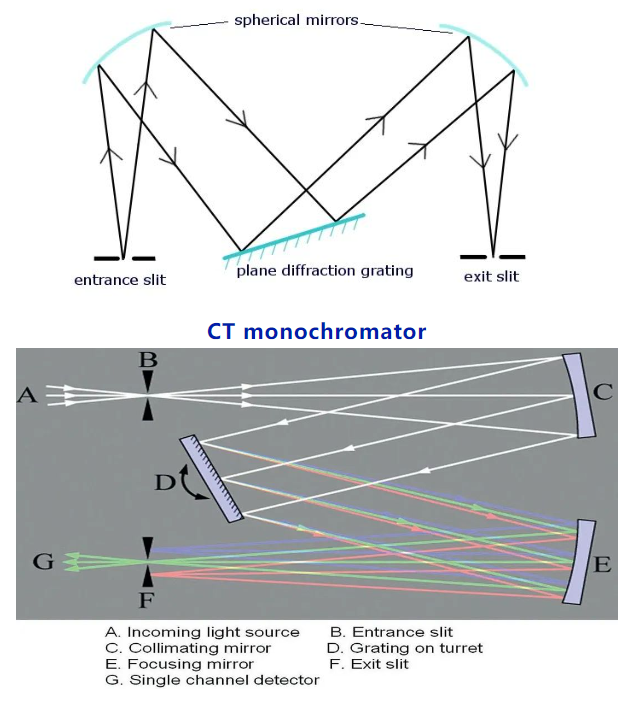
The most common spectrometers in major laboratories are C-T structures, and this class of spectrometers is also called monochromators, which are mainly divided into two categories:
1, symmetrical off-axis scanning C-T structure, this structure is the internal optical path is completely symmetrical, the grating tower wheel has only one central axis. Due to complete symmetry, there will be secondary diffraction, resulting in particularly strong stray light, and because it is an off-axis scan, accuracy will be reduced.
2, asymmetric axial scanning C-T structure, that is, the internal optical path is not completely symmetric, the grating tower wheel has two central axes, to ensure that the grating rotation is scanned in the axis, effectively inhibit stray light, improve the accuracy. The design of the asymmetric in-axis scanning C-T structure revolves around three key points: optimizing image quality, eliminating secondary diffracted light, and maximizing luminous flux.
Its main components are: A. incident light source B. Entrance slit C. collimating mirror D. grating E. focusing mirror F. Exit (slit)G. photodetector
Spectroscope (Spectroscope) is a scientific instrument that breaks down complex light into spectral lines, consisting of prisms or diffraction gratings, etc., using the spectrometer to measure the light reflected from the surface of an object. The seven-color light in the sun is the part of the naked eye can be divided (visible light), but if the spectrometer will decompose the sun, according to the wavelength arrangement, visible light only accounts for a small range of the spectrum, the rest are the naked eye can not distinguish the spectrum, such as infrared, microwave, ultraviolet, X-ray and so on. Through the capture of light information by the spectrometer, the development of photographic plates, or the computerized automatic display of numerical instruments display and analysis, so as to detect what elements are contained in the article. This technology is widely used in the detection of air pollution, water pollution, food hygiene, metal industry and so on.
Post time: Sep-05-2024





