New high sensitivity photodetector
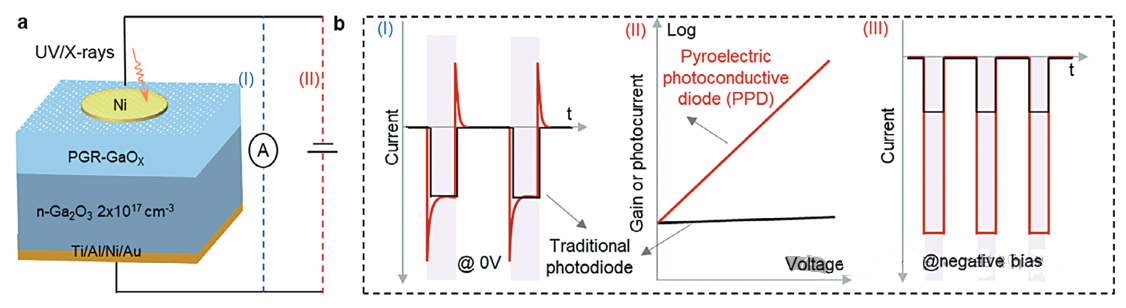
Recently, a research team at the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) based on polycrystalline gallium-rich Gallium oxide Materials (PGR-GaOX) proposed for the first time a new design strategy for high sensitivity and high response speed high photodetector through coupled interface pyroelectric and photoconductivity effects, and the relevant research was published in Advanced Materials. High-energy photoelectric detectors (for deep ultraviolet (DUV) to X-ray bands) are critical in a variety of fields, including national security, medicine, and industrial science.
However, the current semiconductor materials such as Si and α-Se have the problems of large leakage current and low X-ray absorption coefficient, which is difficult to meet the needs of high-performance detection. In contrast, wide-band gap (WBG) semiconductor gallium oxide materials show great potential for high-energy photoelectric detection. However, due to the inevitable deep level trap on the material side and the lack of effective design on the device structure, it is challenging to realize high sensitivity and high response speed high energy photon detectors based on wide-band gap semiconductors. To address these challenges, a research team in China has designed a pyroelectric photoconductive diode (PPD) based on PGR-GaOX for the first time. By coupling the interface pyroelectric effect with the photoconductivity effect, the detection performance is significantly improved. PPD showed high sensitivity to both DUV and X-rays, with response rates up to 104A/W and 105μC×Gyair-1/cm2, respectively, more than 100 times higher than previous detectors made of similar materials. In addition, the interface pyroelectric effect caused by the polar symmetry of the PGR-GaOX depletion region can increase the response speed of the detector by 105 times to 0.1ms. Compared to conventional photodiodes, self-powered mode PPDS produce higher gains due to pyroelectric fields during light switching.
In addition, PPD can operate in bias mode, where the gain is highly dependent on the bias voltage, and ultra-high gain can be achieved by increasing the bias voltage. PPD has great application potential in low energy consumption and high sensitivity imaging enhancement systems. This work not only proves that GaOX is a promising high energy photodetector material, but also provides a new strategy for realizing high performance high energy photodetectors.
Post time: Sep-10-2024





